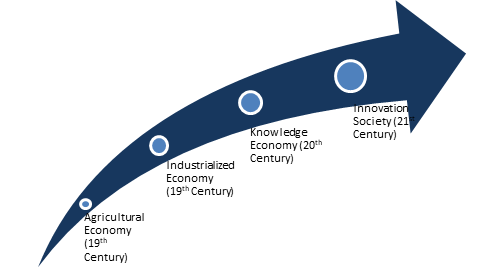
Although the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR) was publicly announced in Davos in 2016, various elements related to what makes this new dimension has been ongoing for almost a decade. The term received wide publicity when German Chancellor Angela Merkel highlighted at the Hanover Fair in 2011, the emergence of Industry 4.0 to make German manufacturing more competitive.
Emergence of Industry Revolution 4.0
Industry 1.0: (1784) : Based on mechanical production equipment driven by water and steam power.
Industry 2.0: (1870): Based on mass production enabled by the division of labor and the use of electrical energy.
Industry 3.0 (1969): Based on the use of electronics and IT to further automate production.
Industry 4.0 (today): Based on the use of cyber-physical systems.
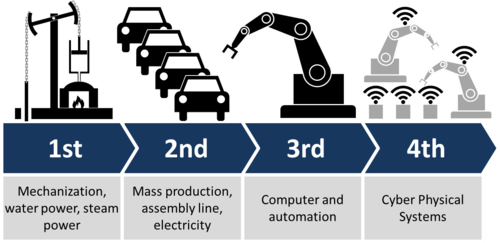
The reason to say that the fourth industrial revolution is in full force today is due to the fact that velocity and impact of current breakthroughs is like never before. The innovations and advances are omnipresent led by strong emergence of fields like Artificial Intelligence, Robotics, Internet of Things, Autonomous Vehicles, Biotechnology, Nanotechnology, 3-D Printing, Material Science, Quantum Computing and Energy Storage. The impact of such breakthroughs is so rapid that the fourth industrial revolution is evolving at an exponential pace, and disrupting almost every industry.
Opportunities brought by Fourth Industry Revolution
Industry 4.0 can play a vital role in raising the global income levels and take our current stand of living to a next orbit. Technology has made it possible to make products and services that enable us to lead a better life. This will drive gains within the efficiency and productivity of our current lifestyle, leading to:
- Increase in global income levels
- Enhanced quality of life with higher order technologies
- Reduction in transportation and communication costs
- Creation of new products and markets
- Safer workplace as hazardous work is taken over by robots
- Enhanced health services leading to longevity
Challenges of Fourth Industrial Revolution
On the contrary, one of the biggest challenges is that it could lead to even higher inequality, as emerging technologies take over labour intensive jobs. But, then Economist Eric Brynjolfsson has famously said, “Technology has always been destroying jobs, and it has always been creating jobs.” Apart from this, the other challenges could be:
· Security issues of data and maintaining privacy
· Risk of greater inequality in labour markets
· Decrease in real income of workers as machines take over
· Displacement of workers by machines and artificial intelligence
· Creation of higher order human jobs is always a concern when automated technologies takeover day to day jobs
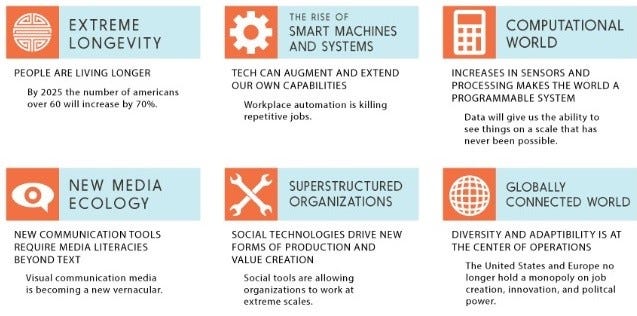
The Six Drivers of Change in workplace brought by Fourth Industrial Revolution
The Fourth Industry Revolution with its opportunities and challenges will bring to the forth the new drivers of change in workplace and organizations. These are summarized in the info-graphic below:
The Skills of Tomorrow needed in the 4IR world
With the drivers of change as enumerated above, the skill-set that would be required by the “jobs- of –the- future” would change rapidly. Some of these skills are specified in the following info-graph.
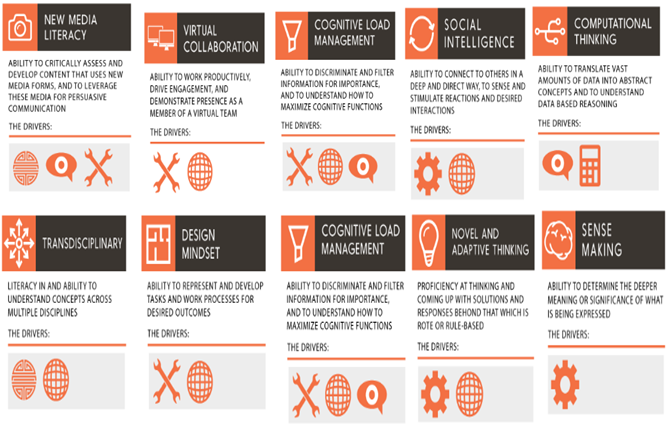
The points to ponder here is whether our education framework today can lead to development of such skills, which will also meet the aspiration of our Generation ‘Z’, who will cut their teeth in 4IR world.
Aspirations of Gen Z
Gen Z is defined as teenagers ages between 13 to 19 currently. They are growing up in a time so revolutionized by technology that it hardly resembles that of their parents and grandparents. This is the generation that would be attending colleges in the coming years!!

In a recent survey conducted among this generation, three notable aspirations came out strongly; about 22% of them expressed desire of relevant and meaningful education to equip them for jobs of the future; about 38% wanted strong growth early enough in their careers and another 32% wished most of their dreams to be fulfilled within 10 years of their entering the new age exciting career.
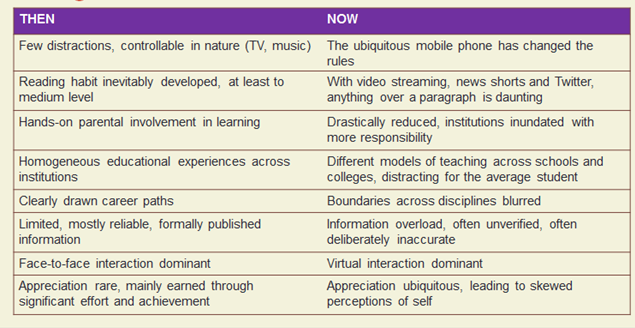
Changed Habits of Gen Z
We now come to issues of how the current Generation Z has changed from those of the earlier generations in terms of reading and learning habits. The table below summarizes these changes:
Need for Education 4.0 framework
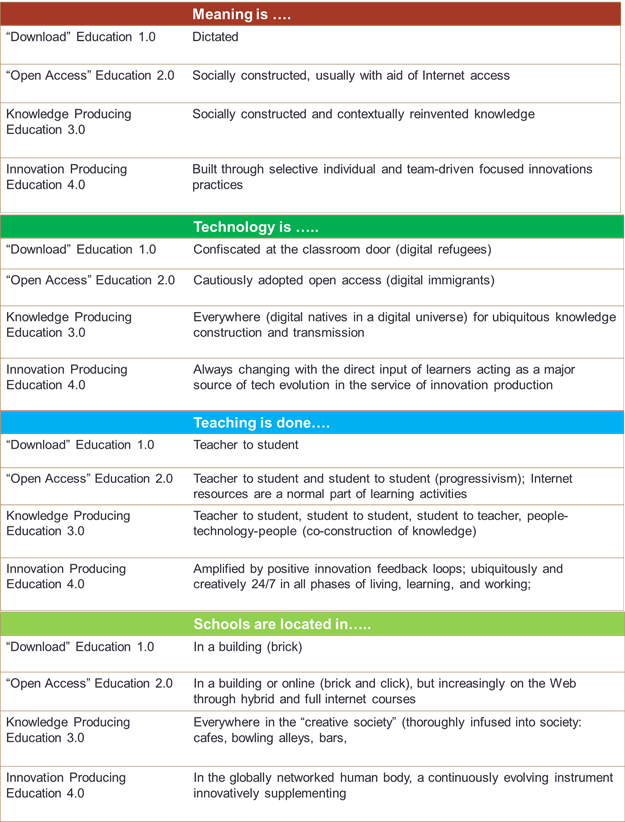
One of the imperatives of the 4IR is human capital enhancements to be able to meet the knowledge and skills requirements. This, as we saw in previous section, puts demand on knowledge production and innovation applications of knowledge. Also, changes in reading and learning habits need that educationalists devise new pedagogical techniques. The rapid pace of emergence of Industry 4.0 requires that Education 4.0 also leapfrogs from the current Education 2.0 framework to Education 3.0/4.0.
Education 1.0: centuries of experience with memorization
Education 2.0: Internet-enabled learning
Education 3.0: Consuming & Producing knowledge
Education 4.0: Empowering education to produce innovation
Evolution of Education 4.0
Following tabular representation depicts the stages of evolution of education over the years. This construct shows how things have changed from education 1.0 to the emerging education 4.0 paradigm.
5 I’s of Learning in Education 4.0
A learning framework is presented below which is aligned to changed habit of Gen ‘Z’ and need for an innovation producing education.
- IMBIBING : Internalizing basic concepts
- ITERATING: Practicing fundamental skills rigorously
- INTERPRETING : Taking facts from study and applying them to different situations with adaptive alterations
- INTEREST: Developing enough curiosity about a subject so as to delve deep and create further body of knowledge
- INNOVATING: Think differently and come up with original concepts and build innovative ideas, products and services
Building the I’s in Education 4.0
Now, let us briefly dwell on how the various facets of the learning model will operate.
Imbibe— from different sources
- Boredom sets in easily for today’s students, there need to infuse excitement from visual and aural inputs
- Use multiple sources — the Internet is your best friend, films, experiences
- Change source material year after year keeping the curriculum at the leading edge.
Iterate— through fun
- Gamify tests — run them as competitions
- Subject championships as teams, evaluated through the year
- Redefine assignments — as challenges where more and more elements of knowledge can be synthesized.
Interpret
- Form student teams and give open-ended projects involving sports or other avenues. For example, while teaching Economics basics, let students do a project on valuation models for football or Kabaddi players.
Interest
- Cover one part of a concept in class, get a group of students to deliver the remaining part. Different group for each concept. This removes stage fright and makes them willing participants too.
Innovate
- Go cross-discipline. Groups of teachers amalgamate subjects to craft year-long projects with a presentation month.
Building Undergraduate program in context of E4.0 and 4IR
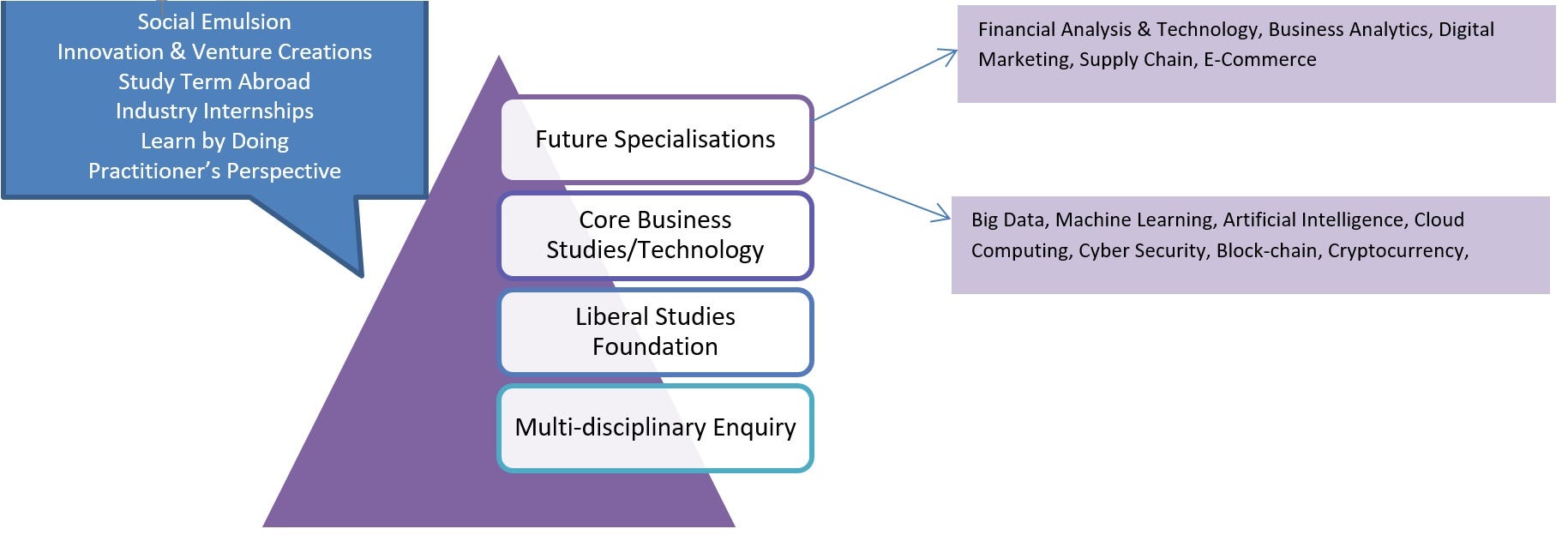
Programs designed to produce Professional Triathletes who can excel in many dimensions that would be needed for the workforce of 4IR
- Core of Business or Technology Discipline
- Specializations for careers of tomorrow
- Digital Marketing, Business Analytics, Machine Learning & AI, Internet-of-Things, Financial Technologies, etc.
- Liberal Dose of Liberal Studies
A truly well-rounded personality building experience — courses on Literature, Performing & Visual Arts, Public Policy, Psychology, Sociology, Media, Design
• Learning by Doing
• Social Sector Internships, Study-Abroad Terms, Industry Engagement
Pedagogical Approach in world of E4.0
From rote to rigor : Not remembering the right answers, it’s about figuring out the right questions
• It’s not about YOU: Emotional Intelligence supersedes individual brilliance. Learn in teams, grow as teams.
- Creators shall inherit the Future: Schools and institutions must pledge NEVER to shoot down ideas. Foster creativity by open-ended questions that take greater time to evaluate but lead to true thinking and real innovations
— — — — — –
References:
1. https://industry4magazine.com/the-beginners-guide-to-the-industry-4-0-f45b93a95649 author : Corné Duivenvoorden
2. https://www.strategy-business.com/article/10-Principles-for-Leading-the-Next-Industrial-Revolution: author Norbert Schwieters and Bob Moritz
3. http://cdn.theatlantic.com/static/front/docs/sponsored/phoenix/future_work_skills_2020.pdf

Preamble
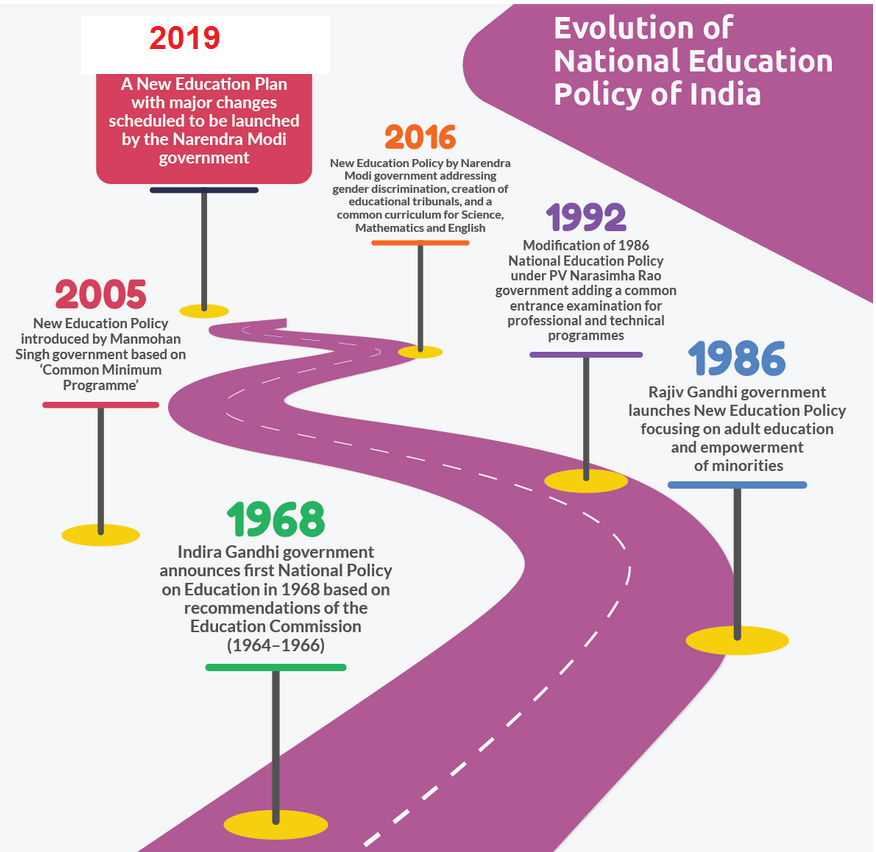
Several Education Policies have been announced by the Government of India from time to time since independence, to promote the access and equity to education for the people of India. These policies covered varied aspects of our country’s large education scenario from elementary education to college education in rural and urban areas. The first version National Education Policy (NEP) was enacted in 1968 by Indira Gandhi government and after an interval of almost two decades a new version was announced by Rajiv Gandhi government 1986. Post liberalization, another new version came in 1992. Over the last three decades, several changes have been made in the governance and planning and management of education that demanded a comprehensive policy reform. This period also witnessed a large growth in participation of private sector in both secondary and tertiary education. This private participation in a way contributed to doubling of GER (Gross Enrollment Ratio) from 12% in the early 1990s to the current figure of 25%.
Intent of Government Behind the New Education Policy 2019
The Government wants to come up with a reformative national education policy to meet the aspirations of young population which is supposed deliver demographic dividend. It seeks to provide framework for developing quality education, innovation and research in order to address the imbalances in demand and supply of skilled manpower.
The overarching aim is to make India a knowledge superpower by equipping students with the necessary skills and knowledge.
The National Education Policy 2019 is currently a draft document that proposes a fundamental shift in the education landscape of India. A Committee chaired by former Indian Space Research Organization Chief, Prof. K Kasturi Rangan had submitted the draft of the new NEP. Earlier another committee, headed by former Cabinet Secretary TSR Subramanian had submitted a draft new education policy in 2016 which did not find much favour among the various stakeholders.

The draft NEP 2019 has following key elements
- Art, music, crafts, sports, yoga and social service should form part of the main curriculum apart from these endeavours as co-curricular and extra-curricular activities.
- Equal treatment of government and private educational institutions, in terms of regulations and funding.
- Comprehensive reorganization of undergraduate program, over the years the most of programs should be of four-year duration following the best practices elsewhere in the world. This will also help enriching the undergraduate curriculum with proper infusion of liberal study courses.
- Introduction of an integrated 4 year BA.B.Ed/B.Sc.B.Ed programs as per-requisite qualifications for school teachers.
- Creation of Rashtriya Shiksha Aayog (National Education Council) to regulate the education sector and subsume some of the current powers of MHRD.
- Special Regulatory Systems for Professional Education Areas.
- States can set up Rajya Shiksha Aayog or State Education Commission on lines of NEC.
- National Research Foundation for strengthening research funding and outcomes.
- National Higher Education Regulatory Authority for Higher Education in place of UGC.
- Vocational courses should be made compulsory in secondary school curriculum and vocational degrees could be granted by Higher Education Institutions (HEIs)
- The National Educational Technology Forum should be formed which would help HEIs in finding and applying appropriate education technology solutions.
Reformation and Unification of Higher Education Institutions (HEI)
Another important recommendation of Committee that higher education would require a new approach for what constitutes an HEI, i.e. a university or a college. It suggests that University has only one definition worldwide, hence the present complex nomenclature of HEIs, such as Deemed University, Affiliating University, Unitary University, etc should be phased out. Also, universities should be distinguished from degree-granting colleges by the fact that they offer graduate programs in a broad range of subjects and have larger enrollments.
Meanwhile, a college should be restricted to be a multidisciplinary institution of higher learning primarily focused on, though not restricted to, undergraduate teaching, and it would generally be smaller than a typical university. The Policy states that all HEIs should evolve into one of these three types of institutions, which will be referred as Type 1: Research universities, Type 2: Teaching universities, and Type 3: Colleges. All affiliating universities will be transformed into Type1,2 universities. All HEI should be universities or degree-granting autonomous colleges. The concept of affiliating university and affiliated colleges should be phased out over next 12 years. The report further recommends that the Universities offering single stream may be phased out and all universities should become multidisciplinary HEIs. Autonomous colleges should have freedom to grant their own degrees.
Incorporating liberal arts and flexibility in curriculum

The Policy highlights the importance of liberal arts education which has indeed become extremely important in view of the kind of skills set that jobs of the future need. These include social intelligence, new media literacy, virtual collaborations, cognitive load management, trans disciplinary etc.
Special Bachelor’s degree options — a 4- year Bachelor of Liberal Arts (BLA) or Bachelor of Liberal Education (BLE) nomenclature to develop liberal studies disciplines is envisaged in the policy. Though traditional B. A, B. Sc, B.Voc., would continue but all bachelor’s degree would eventually move towards integrating to a liberal education approach. The policy draft also suggests for 5-year integrated program wherein students completing a 4-year BLE with Research, could opt for 1-year Masters. PhD would require either Master or 4-year Bachelors with Research.
Autonomy on Curriculum, Pedagogy and Assessment

The current Choice Based Credit System (CBCS) framework revised and improved, to make clear basic vision while leaving plenty of room for innovation and flexibility. Today’s generation which is entering institutions of higher learning are increasingly looking forward to build ‘Bespoke degrees’ wherein the key skills set that they wish to acquire in line with jobs of the future. Proper implementation of CBCS will lead to flexibility of education and methodology to build customised degrees.
Quality of Open and Distance Learning (ODL)

The access and opportunities for distance learning curriculum and pedagogy required to be made qualitative in terms of –
i. Transformation of ODL:
a. The make ODL programmes of the highest quality it should be made qualitative at par with the institutional programmes
ii. Leveraging of ODL:
a. Improving the quality of learning experience by including professional and vocational education, life-long learning and certification and supporting development of teachers.
iii. Ensuring Quality of ODL:
a. By way of using highest-rated faculty, courses, and programmes to produce the highest-quality contents for curriculum and pedagogy.
Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs) as Learner support services
MOOCs make high-quality educational content available to the masses, leveraging videos, quizzes, and discussion forums typically within a four to six-week course session. Further, one’s location doesn’t matter, if one has a high bandwidth internet connection. Moreover, classes are self-directed, so they can fit around one’s schedule. It ensures proper student assessment and development of a mechanism for feedback and performance.
The importance of online education is rightfully endorsed by the new NEP policy. It suggests that MOOCs offered by universities anywhere in the world should be suitably recognised, after ascertaining the alignment of their contents with the National Higher Education Qualifications Framework (NHEQF), and appropriate checks on their delivery methods, modes of interaction with students, and assessment procedures. MOOCs are being developed by premier institutions such as Stanford, Yale, Michigan, and Imperial College London, and others in the same league to deliver content to individuals around the world.
The world class MOOC platform like Coursera have created a specialized offering known as Coursera for Campus (C4C) which is providing online courses for credit use.
As a part of the new NEP, “MOOCs” should be institutionalized at all HEIs offering ODL. The report recommends that the HEIs should be encouraged, through funding and other support mechanisms, to put some of their best courses online. The policy also envisions that going forward, good institutions would be able to offer fully online degrees.
Conclusion
Though it is acknowledged that the policy document is a good beginning, but implementation needs to be done in a manner which will make an impact on future generations.
The direction towards autonomy is still not very clear as plethora of new so-called regulators are being considered by this draft, such as National Education Council (NEC), State Education Council (SEC), General Education Council (GEC) and National Higher Education Regulatory Authority (NHERA). We hope that institutions will not get swamped in this quagmire.
Another point is the openness and willingness to convert open distance learning into a true implementation of online education. The current regulations in this respect are very binding in nature, especially in terms of usage of SWAYAM/NPTEL platforms. The institutions going forward under the NEP should have independence of sourcing, developing and using platform of their choice to disseminate online education.
The new policy should be unequivocal about the duration of undergraduate programs; on one side it says that UG degrees should be four year yet it juxtaposes with continuance of three year BA / BSc degrees.
Policy draft also speaks a lot about liberal studies. However, how to intersperse such education with existing technical and business education, there is no clarity.
Given that it envisages a massive and rapid restructuring of higher education, it would be useful to know how the actual framework would operate otherwise the Indian education would continue to be emasculated by rigid regulatory regime.
Reference: Draft National Education Policy 2019
The modern world is full of complexities and the only constant thing is change. Currently, the ‘disruptive innovation’ has become synonymous with progress, wherein business models look completely different from those that exist in traditional setups. Many believe that we live in a VUCA world; the acronym initially coined by the US Army to refer ‘volatile, uncertain, complex and ambiguous’ environment. Are we, as Universities or higher education institutions, equipped to train students who can navigate this unpredictable minefield that the world is becoming? This lack of predictability regarding the events and their impact on our lives has led Universities to think about flexible education models.

Many educators and recruiters believe that future jobs are likely to be taken over by robots, artificial intelligence, IoT devices, autonomous vehicles amongst other technologies. A recent study at Oxford University states that about 47% of all-American jobs are at high risk of getting automated by early 2030, less than 10 years from today! The statistics certainly conveys a sense of doom and danger as it has universal repercussion, especially for a populous country like India. However, some researchers in the field of automation highlight that the jobs which fall into three ‘D’ categories, namely the dull, the dirty and the dangerous would eventually be taken over by the machines. Positively, this transition could lead to giving more space for human creativity and imagination to do the things which we humans are good at it and thus add value to the economy.
Nevertheless, the quintessential question arises, how can graduates of the future cope up with these changing times?

Therefore, Gen Z which are entering institutions of higher learning is increasingly building ‘Bespoke degrees’ wherein the key skills set that they wish to acquire in line with jobs of the future. Let us investigate as to how this development can be facilitated.
Flexible Education: A cornerstone to build Bespoke Degrees.
To build a fully flexible system of education, one needs to investigate flexibility along the following five dimensions:

Flexibility in Time explores possibilities of Program start and finish times to be flexible and not be bound to rigid semester schedules. Similarly, the length and pace of various academic programs can also be flexible leading to multiple assessment points and number of annual study periods.

Flexibility in Content implies that Program topics and their sequence can be modified by a specific learner. The types of learning materials, as well as assessment rubrics, can also vary with the need for a learner.
Flexibility in Access Requirements indicates that there could be multiple program entry and exit points as well as recognition of prior learning experience (RPL/E) and the possibility of using bridge courses as well as articulation into other programs.
Flexibility in Instructional Design means that learning mode (group, individual/independent, face-to-face), learning styles (slow, fast, aural, visual, simulated), language(s) of instruction learning delivery modes (lecture notes, printed study guides, recorded lectures) can be customised by using multiple providers of learning resources (teacher, students, library, internet, experience).

Flexibility in Delivery implies that learners can choose from amongst:
• Places of study
• (on-campus, off-campus, online, blended, offshore/twinning, work-based learning)
• The social organisation of Learning
• (contact with instructors and/or other students or individualistic)
• Methods of support and forms of assistance
• (Tutorials, FAQs etc)
• Content delivery channels
• (Physical, Online, Offline, Multimedia, Experiential etc)
• Access to program administrative information and processes
- (Physical, Online, Offline)
MOOC: A definite mode to assist Flexible Education
Massive open online courses (MOOCs) are being developed by premier institutions such as Stanford, Yale, Michigan, and Imperial College London, and others in the same league to deliver content to individuals around the world.
MOOCs make high-quality educational content available to the masses, leveraging videos, quizzes, and discussion forums typically within a four to six-week course session. Further, one’s location doesn’t matter, as long as one has a high bandwidth internet connection. Moreover, classes are self-directed, so they can fit around one’s schedule.
MOOCs reach wide audience cutting across cultures, professions, ages, and education backgrounds. Several MOOC providers have come to the fore to meet this broad audience. Among the most prominent providers are Coursera, edX, FutureLearn, Udacity, and Udemy.
Curating Content for Building Bespoke Degrees
As depicted in the graphic below, the flexible education model in the Universities of tomorrow coupled with the availability of MOOCs which can be integrated the next generation are curating their academic programs in the context of the needs of the 4th Industrial Revolution. Such programs are usually referred to as 4.0 programs in the context of Education 4.0 and Industry 4.0.
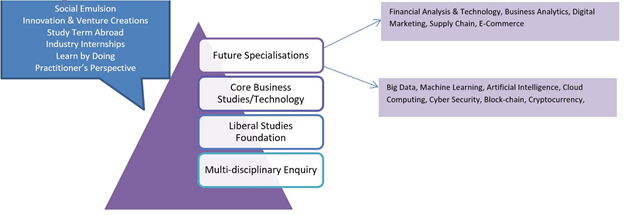
Such programs can be customized to produce Professional Triathletes who can excel in many dimensions that would be needed for the workforce in a VUCA world. This may include:
- The core of Business or Technology Discipline
- Specializations for careers of tomorrow
- Digital Marketing, Business Analytics, Machine Learning & AI, Internet- of-Things, Financial Technologies, etc.
- Liberal Dose of Liberal Studies
- A truly well-rounded personality building experience — courses on Literature, Performing & Visual Arts, Public Policy, Psychology, Sociology, Media, Design
Some of the MOOC providers are now developing special offerings of their courses to enable Universities to provide special cutting-edge content for their students. This helps students to add-on the emerging skill areas to their baseline degrees. One such example is Coursera who has developed a special offering for university campuses called ‘Coursera for Campus’ (C4C). One of the early adopters of this offering was Manipal Academy of Higher Education (Deemed University). The case study of this relationship and its outcomes follows: –
Case Study
CHALLENGE AREA FOR THE UNIVERSITY
Enabling a learning environment for students to keep up with the latest skills
In a world which is experiencing an agglomeration of factors such as industry 4.0, digital technologies and sustainability shaping its near- and long-term future, liberal education is expected to empower individuals and prepare them to deal with complexity and constant change. It provides students with a broad knowledge of the wider world (e.g. science, culture,and society) as well as in-depth study in specific areas of interest. Manipal Academy of Higher Education (MAHE) intended to create such an environment in its campus where students can pursue their personal and career aspirations along with their formal education. This was indeed progressive thinking by the University as to how to maintain the currency of content in a 3 to 4-year degree program.
MAHE chose to create a multi-disciplinary learning environment which made it possible for a student from a non-computer science background to pursue data science or for a doctoral student to pursue music. They wanted to enable an option for students to pursue learning in areas of their passion apart from their current degree program. They could also embellish their degree with add-on super-specialized emerging areas, leading to better employability.
PARTNERSHIP SOLUTION
Blending classroom learning with Coursera courses
MAHE wanted to partner with a learning provider who could provide relevant content from world-class institutions and blend it with expert pedagogy and technology that lets students learn anytime, anywhere. Therefore, Coursera came with a solution which evolved into ultimately C4C.
Coursera partnered with MAHE to develop a program with three objectives:
- To provide learning across different disciplines to over 20,000 students studying at various institutes under MAHE Manipal
- To provide an opportunity for faculty members to upskill and reskill across various domains
- To provide for-credit learning at different schools and colleges
This relationship provided an opportunity for their students to choose amongst the thousands of courses available on Coursera. As the Coursera platform has courses at all levels — beginner, intermediate, advanced as well as Specializations which make it convenient for students to embed courses at an appropriate level and earn credits.
OUTCOMES
Multiple outcomes emerged for various stakeholders of the university including the teachers and the students.
MAHE defined the success of this program based on each of the key stakeholders — the University, the faculty and the students.
The University management was looking to provide an environment in which students were able to learn what they want to learn. The faculty members wanted an opportunity to blend the quality content available online with the curriculum in the classroom. For students it was important to address questions such as-are they able to get an internship of their choice, are they able to pursue a career of their choice and are they able to get a job when they graduate?
The Coursera program for Manipal has helped meet the objectives of these stakeholders.
Over 69,000 courses have been enrolled in by students and faculty members across various campuses of Manipal Group. Nearly 70 courses have been inducted into the blended learning pedagogy for-credit. Almost 200,000 hours of learning has happened via this program making it one of the largest learning programs on Coursera. The students found that Coursera content has made a positive career impact for them.
They have learned and acquired skills that they couldn’t acquire otherwise and have thoroughly appreciated the flexibility of the online learning process.
(Source: Coursera India Private Limited)
Conclusion
Sensing the urgency of the imminent threat in the future job markets as well as the changed mindset of the upcoming generation, most countries are being forced to revisit their existing education policies and find measures to tackle the employability quotient. India is no different and the draft version of the new education policy (NEP) is a step in this direction. The policy attempts to address relevant changes required in the modern education system in the higher education segment and keeping in view with the emerging needs of Industry 4.0. A paradigm shift is suggested by it which places a great emphasis on online education as well as MOOCs. The policy recommends how online learning can be made integral to mainstream education. This indeed is a heartening step for the country.
]]>Are Cyborg Universities coming soon?
Universities and colleges world over are struggling to find the ways to attract new students in the wake of Covid-19 pandemic. Several of them have extended their deadlines for accepting application and enrollment. A paradigm shift in the education about the value, price and program has become obvious in these days.
Many feel that the value of education has been substantially degraded, this is because in today’s consumerist world, education must lead to an employability outcome.
Education for sake of broadening one’s horizon and for learning is becoming passé. Students are forced to take a hard look at that the fee they are going to spend for any university degree vis-à-vis the return on investment (ROI).
Growing uncertainties regarding the filling up of seats giving a nightmare to academic administrators across the universities. This pandemic has disrupted the staid firmament of the education sector.
Are our universities are equipped to deal with the rapid change in the landscape of higher education?
Many educational experts agree to the fact that the world order of higher education is no longer going to be same as before. According to Professor Scott Galloway of NYU Stern School of Business, a major shift in the landscape of higher education is inevitable, as the giant tech companies such as Google, Facebook, Apple would necessitate partnership with the top elite universities around the world to offer degrees to students across the globe. Such partnership will enable these marquee institutions to expand enormously their student intake by offering hybrid online-offline degrees which are economically affordable while not compromising the value of their degree. He asserts that these associations will challenge the very existence of brick-and-mortar universities and eventually will replace most of these universities sooner or later.
Even though delivered mostly online, this imminent disruption will find more people to have access to a solid education never than before. The partnerships will make life easier for hundreds of millions of people. The face-to face system of learning that has evolved over centuries will be faded away.
People may wonder why the large technology companies, for example Apple should invest in a collaborative partnership with one of the Ivy League universities, say MIT. Answer is rather obvious because education is the next growth driver for such companies to move to next higher scale.
“These big-tech companies have to turn their eyes to new prey, the list of which gets pretty short pretty fast if you look at how big these industries need to be in that weight class. People ask if big tech wants to get into education and health care, and I say no, they must get into education and health care. They have no choice”. Professor Galloway argues.
This arrangement will lead to so-called “Cyborg Universities” a confluence of cyber-physical marriage of technology with brand and reputation of big-name red brick universities.
However, some academicians do not favour this argument that Google, Apple, and Microsoft will soon partner with top tier universities to corner the market on higher education and leave the remaining universities and colleges in the dust.
Counter Point
One such counter argument by a prolific blogger Pete in Medium says,
“I remain optimistic (that) on-campus education will return. The traditional role of college as a place for emotional development cannot be underscored enough. Entering a new social environment, without the baggage of your past has always been a critical part of development. It allows you to explore and discover what inspires you. Sure, some people are popular and confident no matter where they are, they know exactly what they want to do and never deviate. But those students are surely a minority, (and) do not always turn out successful, and are not necessarily someone you would want to spend time with. The in-person campus will continue to be a place where kids want to go, and parents will see value. Remote learning will hopefully attenuate the cost of education, but it will not result in an end to in-person education anytime soon. That’s my guess.”
Accelerated Adoption of Technology in Higher Education
The academic world is still in its nascent stages of remote learning and the ongoing pandemic will accelerate this technology enabled delivery of education. To optimize the enrollments, many universities have been revamping the pricing of on-campus degrees (traditionally more expensive) and online degrees/certifications (generally thought to be cheaper). In the emerging environment, there would be experimentation with hybrid model, implying credits of degrees can be earned partly on campus and partly through online methodology. The price point may also lie somewhere in-between.
In India, also the regulators (UGC) permitted up to 20% of courses to earn online. The New Education Policy has provisions to enable universities offer fully online degrees.
Currently, many established online course delivery platforms exist, like Coursera, edX, Udacity and in India home grown platforms like NPTEL and SWAYAM. These platforms constitute the segment of remote learning called MOOCs (Massive Open Online Courses). Recently, Coursera has launched C4C (Coursera For Campus) initiative in India. Here, universities take bulk licenses from Coursera and their students can enroll for certain number of courses to earn credits towards their degree. This initiative became popular during the pandemic days as it was offered at no-cost to universities which helped them experiment with this way of learning.
So, how the universities in India should prepare to stay valid and relevant in the digital disruption and radical change in the emerging teaching learning paradigm.
Evolution to University 4.0
Revolutionary change should be necessitated to sustain in the challenging years to come, and transformation into University 4.0 could be an appropriate description of the ways that universities around the world need to respond to the new economy.
Key Elements of University 4.0
The adoption of U4.0 concept would entail development of curriculum appropriate to skills needed for sustaining Industry 4.0 skill requirements. This will lead to development of curriculum 4.0. The pedagogy would transform to education 4.0 to imbibe concepts of digital teaching learning incorporating the use of online resources. It would also lead to co-creation of knowledge and innovation.
Key to this a development of a digital platform for teaching learning which incorporates technologies such as AR/VR and AI&ML based adaptive learning so that today’s digital natives get exemplary student experience.
Distinctive learning models catering to multidisciplinary programs, such as adoption of flexible education and HBO (hybrid-blended-online) model are the imperative in this concept. Flexible education offers more efficient educational delivery model, provides marketing advantage as distinctiveness, may attract more enrollments thereby meeting requirement of today’s students who need more individuality of time, place and mode of study and widens the access of HE through Flexible Delivery Mode. Adoption of full-blown Choice Based Credit System (CBCS), Be-Spoke Degrees, MOOC Integration and Experiential Learning are to be carefully curated in the modern teaching learning experience.
With wide-ranging developments in technology and its disruptive influence on emerging models of higher education it is matter of time when University 4.0 will morph into Cyborg Universities, the shape and form only time will tell.
“We need technology in every classroom and in every student and teacher’s hand, because it is the pen and paper of our time, and it is the lens through which we experience much of our world.” — David Warlick
Author: Dr. Parag Diwan is a noted academic leader and has many large institution building projects to his credit. Currently, he works with multiple universities to make the higher education relevant to today’s digital economy.
The world has progressed through many eras of industrial revolution. Beginning in 1784, when the steam engine was harnessed by the invention of the steam engine by the Scottish Inventor, James Watt, to the current age of Industrial Revolution 4.0, where cyber-physical systems are coming to the fore. All this is thanks to the enormous efforts of engineers who have led several of these advances and thereby laid the foundation of the global economy.
Many of today’s technologies and products have at least some element of creativity involved in their creation, paving the way for people to lead long, rewarding, and secure lives. In today’s rapidly evolving engineering landscape, we have an increased obligation to transform the undergraduate educational experience from the traditional pedantic curriculum in explicit disciplines to a broader foundational experience for life-long success.
What ails the of Engineering Education today?

Today, the engineering education landscape is impacted by VUCA (volatile, unpredictable, chaotic and ambiguous) forces. This has widened the gap between the changing avenues of employment and the existing structure of engineering education. Although 25 percent of world’s engineers are in India, statistics reveal that just 20 percent of our engineering graduates are hired by existing businesses. Engineering is among the few professions in which creativity and innovation plays a vital role in its practice. The lack of creativity and innovation skills are what generally pushes these engineers to fall behind in the employability quotient.
“Engineering is among the few professions in which creativity and innovation plays a vital role in its practice”.
Studies further reveal that only 3.84 percent of the India’s engineers have the scientific, cognitive and linguistic abilities needed for entry-level information technology jobs. In fields that are thriving today, such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, data science and mobile growth, only 3 percent of engineers have new-age technology skills. Therefore, only 1.7% of engineers have the expertise needed to work in jobs in the modern century. It has been identified that there are few more reasons which are attributed to India’s engineers’ poor employability; only 40 percent of engineering graduates do an internship, while only 7 percent of students do several internships. In addition to a shortage of internships, since only 36 percent do experiential learning tasks beyond their academic programme leading to non-development of cognitive and innovations skills. Thus, in essence they do not develop solve problems skills.
Another difficulty leading to the poor employability of engineers is that the subject is taught in colleges in a very technical way; 60% of professors do not speak about the implementation of concepts in the industry and only 47% of engineers attend some business discussion.
The number of engineers in the US who know how to code is approximately four times that of Indian engineers, statistics reveal. There are also many other variables in terms of the soft skills that make Indian engineers so seriously unemployable through industries.
Several engineering schools in our country impart education with little practical experience and no concept of creativity or innovation instilled. This is obvious from the fact that the Indian engineering institutions, with a few exceptions, are still struggling to establish a place in the world order.
Therefore, a paradigm shift in the engineering education is important. The shift is from teacher-centered to student-centered teaching-learning systems, content-based education to outcome-based education, employability enhancing skills, instructors to facilitators, conventional engineering disciplines to interdisciplinary classes, chalk and board (lecture-based) technology-driven learning.
Core Engineering Education is losing sheen
Today, only strong values or knowledge are not enough to survive the techno-entrepreneurial boom. Innovative effects must be obtained by engineers with a much larger cross-disciplinary manner. Countries like US, UK, France, Germany, Russia and Singapore are much more advanced and practical oriented than Indian universities, in terms of imparting engineering education. With their highly practical curriculum, they develop basic technological skills of their graduates to prove their value.
Therefore, we need engineers to turn concepts into practice in an advanced technical environment. Our engineers should be trained to create solutions to the world’s toughest engineering problems by incorporating the applications of the concepts of mathematics and science.
Under the wide variety of disciplines of engineering category, no matter what the interest of the prospective students are, one or other facets of engineering discipline will enthuse them to move on the path of becoming an engineer. If you want to it is civil, electrical, chemical or mechanical engineering, the engineering field has a place for you whether you want to tinker, develop, design or construct.
Civil Engineering: Civil engineers have one of the best tasks in the world. Setting up the standard of life. Civil engineers set up, develop, construct and run the structures required for trendy civilization with technological and creative expertise, ranging from highways and bridges to sewage treatment plants and energy-efficient houses. It is the duty of civil engineering to construct rational transport networks of consistency, such as roads, airports, rail lines, ocean ports, etc. A civil engineer is concerned with deciding the right form for these structures and looking at the building process once, so that after completion, the durability of these structures is ensured. Additionally, these systems should be adequate in terms of convenience for the general population. In fact, no field of existence that does not require the contribution of civil engineering can be found.
Electrical Engineering: What would have done if we did not have electricity? In today’s appliance laden world, electrical engineering applications are ubiquitous. The electrical engineer gives us the ability to harness energy that has eased our lives. Electrical engineering covers areas such as electricity engineering, network engineering, network engineering, supervisory control and data processing, robots, software engineering, control system engineering, etc. To achieve this, electrical engineers are responsible for computer technology and design, turbines, transmitting devices, navigation systems, wiring and lighting, electronic device architecture. In making sure the project is safe, a smart electrical engineer plays an important role.
Mechanical Engineering: Throughout the industrial revolution, the invention of advanced machines and their usage led to mass production of goods which also contributed to the exponential growth of mechanical engineering. The jobs in mechanical engineering concentrate on developing inventions that meet human needs. In modern life, nearly any goods or service has undoubtedly been touched in some form by a mechanical engineer to assist humanity. In addition, technology itself has influenced how mechanical engineers work and the suite of software has also become very strong in recent decades. In mechanical engineering, mechanical engineers use software such as fluid mechanics, computer-aided designs with long component analysis. Researchers evaluate the right processes within the sector in order to generate incremental economic activity.
Computer Science Engineering: Also, an increased demand has been generated for computer science engineers with the introduction of information technology and related advancement of computer hardware and applications. This discipline is much more than learning to code. The benefits go beyond knowing a particular programming language. It teaches students about logic, understanding systems and engineering and design basics, all of which are applicable to other academic and career fields.
Historically, engineers took pride in constructing concrete bridges and finding alternate energy sources for sustainable development of the world. But now, the world of virtual effects and cyber-physical systems, it is more that computer science graduates rule the roost.
To revive the core branches, we need to rejuvenate them by creating new specialisms within their broader framework such as Civil Engineering with Smart Cities, Electrical Engineering with IoT and Mechanical Engineering with Additive Manufacturing, Robotics, Automation and so on.
How to Reinvent engineering education methodology
Training of engineering should be capable of inspiring graduates with more than just a deep knowledge of science and technology. To overcome our planet’s hardest challenges, the engineering education should also cultivate independent thinking, powerful communicators, and empathetic and innovative leaders.
“Without having a holistic view of digital technologies and a humanistic approach to addressing real-life challenges, one would never expect to be a new technology pioneer”.
The curriculum, therefore, should embark on unlearning certain old patterns such as rote learning and learn new skills and mindsets. These could be interdisciplinary thought, imaginative mentality, teamwork ability. The curriculum should excite students rekindling their natural qualities such as enthusiasm, questioning abilities and of course their creativity. The curriculum should encourage to develop the basic technical, social and humanistic understanding that every student should have at its core. It should also incorporate the students’ quest for discovery and an increased active role in choosing his path. A faculty adviser could be consulted for opting of a major. Subsequently, pick a real-world problem area of student’s interest. Once the student gains enough depth in the topic, he could concentrate on developing deep proficiency in an field. This will not only create in depth knowledge, but also developing the right skill sets to build impactful solutions. The learners would be able to connect the dots through wide-ranging combination of classes at the intersection of technology, sciences, and liberal arts.
For instance, a curriculum with a core in AI students get to learn, create and apply latest machine-learning models in real-life problems — like, identifying diseases-ridden crops through images etc. But the learning should not stop at AI or ML. There must have another layer on top of the AI wherein either Design Thinking or System Thinking can be taught through class activities, which include relentless hours of brainstorming, prototyping and presentations. This would help the learners to understand problems through a user’s point of view.
Building an Engineering Program in context of Industry 4.0
Keeping in view of the Industry 4.0 revolution, we can think of creating an undergraduate engineering program with Liberal Studies foundation, a strong core of Engineering and Digital Economy expertise. Suggested curricular design should follow the paradigm of blending liberal studies with engineering curricula, rather than bridging, to produce engineering graduates with a broadened horizon.
Some components that may be embedded include Critical Thinking, Historical Perspective, Public Policy, Art Appreciation, Elements of Social and Applied Psychology, and Literature. Exposure to such courses will provide engineering graduates a framework to think more broadly outside the narrow confines of engineering studies and develop abilities to think about and deal with the increasingly VUCA world;in line with need of industry to have “Global, Liberal, Cerebral” graduates. Such engineers will be adept at a global stage with liberal instincts that ingrain in them an intellectual curiosity and cerebral approach to ‘think bigger’ and ‘connect the dots’ in different situations.
Given below a suggested a model that merges liberal studies with engineering education in a way that teaches engineering graduates to think critically and analytically and also provides them with digital economy specific skills.
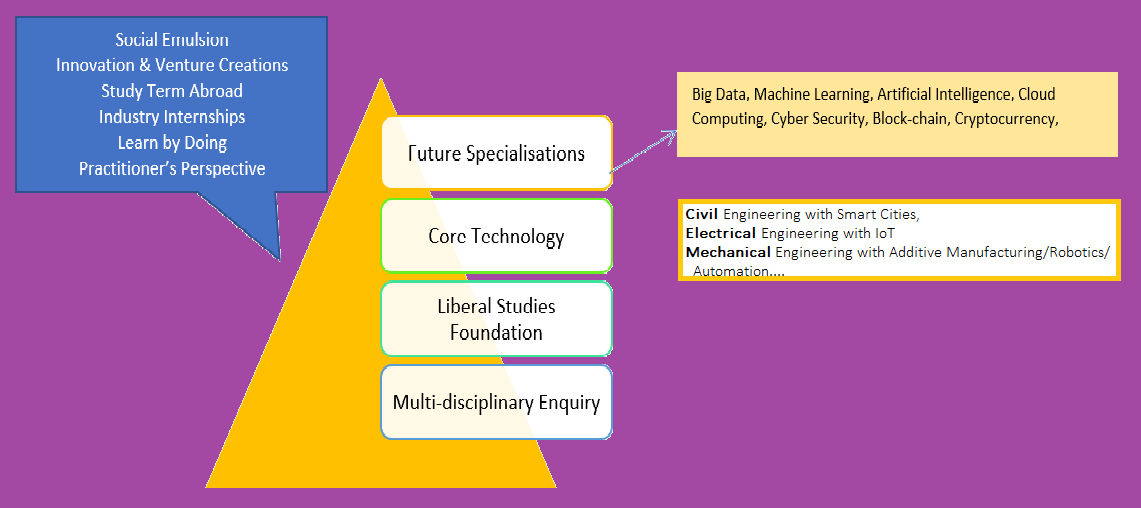
We conclude our discussion on reinventing engineering education with a take on survival of the fittest from the book ‘The Signal and The Noise” by Nate Silver, which states that human have few natural defenses. “We are not all that fast, and we are not all that strong. We do not have claws or fangs or body armor. We cannot spit venom. We cannot camouflage ourselves. And we cannot fly. Instead, we survive by means of our wits. Our minds are quick. We are wired to detect patterns and respond to opportunities and threat without much hesitation” (Silver 2012). Our goal is to develop future engineers that are quick witted and adaptable so that they not only survive but succeed and thrive in the VUCA world.
]]>The discussions and deliberations about online education mostly centered around the technology’s experience and accessibility issues, but during this dialogue, the emerging pedagogy and its features went unnoticed.
The traditional pedagogy, which had hitherto remained largely unchanged despite the technological innovations, have been radically transformed as a post pandemic outcome resulting from the necessity of keeping an access to education through e-learning and online mechanism.
This new pedagogy is being evolved through a continuous process which is making both our teachers and students constantly adapting to this new way of delivering and receiving education.

In this era of e-learning, this evolving pedagogy will help us to realize the new possibilities and complexities. If we consider the delivery of knowledge through digital devices and the internet as the hallmarks of e-learning, then self-paced learning is its enduring nature. Although it is not always evident in the more familiar hybrid (a combination of online and offline models) learning.
Therefore, digital, and autonomous learning needs to be looked at more seriously and without being misled by the awe of technology.
Self-Paced Learning Helps Different Learnability Quotient of Students
Self-paced learning is generally the practice of learning in an environment where the learner sets his or her schedule and adjusts it to his or her convenience and interest. The learner decides how long a lesson will take and how often to sit down and study it. Generally, the institutions or teachers are not involved in this process. While using the features of digital technology, the content of the lesson is accessible to the learner at any place and any time of his choice.

In the traditional learning system, the number of hours of teaching per lesson is limited by a predetermined schedule, from what day, at what time, to ancillary activities and assessments. Students are obliged to complete the learning process accordingly. Students who fail to complete these steps successfully according to the academic calendar will be considered a failure.
But, in self-paced learning methods, reasons of failure due to inadequacy of time is rare and often improbable.
Redefinition of the Role of Teachers
The self-paced learning method may not be reduced only to the learners’ control-over-the -timing of the learning process. The general perception about the framework of education will be radically changed both the course as well as the direction.
It is important to note that online and digital models create not just a learning activity but also a broader learning environment.
In all offline learning systems, teachers are the ultimate authority. Obedience to authority is determined by the experience of the study as well as the outcome of the examination. In a teacher-centric model, where teachers ‘authoritatively’ impart knowledge and humble students accept it without question. In the exercise of pedagogical power is often unilaterally set time limits. All deadlines apply to a class as a whole. It is not practical for many people to allow different time limits for each lesson, depending on their learning abilities or physical or mental circumstances. Then students who must ask for more time in any particular situation will thereby re-strengthen the ‘authority’ of the teachers.
Fundamentally, in the self-paced learning method, the teacher-centered power structure will be destabilized. In e-learning, teachers relinquish the right to make final decisions about ‘time’ to the student thereby give up excessive powers and become facilitators of the learning process. However, this transition should not be seen as a shortcoming, but as an improvement in teachers’ overall responsibility.
The role of teachers, which used to be limited to taking classes and conducting exams, is now shifting to taking full responsibility for the overall effectiveness of a course. The redistribution of authority in the academic sphere is not a no-confidence motion against teachers, whereas a new mutual understanding of the responsibility that the student must assume for himself/herself. In self-paced learning, the student experiences greater responsibility and flexibility. Teachers who reject excessive authority and students who take more responsibility for their learning will be the starting point for a healthier academic environment, which will enable comprehensive change.
Multi-modal Learning Processes
The most striking difference in self-paced learning is that it positively utilizes the diversity of students’ learning abilities. Each student will grasp things at his speed. Because of the different tastes, each student responds differently to different parts of the same subject. For example, a student who learns the application of mechanics quickly may take longer to understand concepts of strength of materials. When all students are forced to learn all the lessons at the same pace and through the same activities in the traditional way of learning, some go on without understanding the subject and some without understanding at all. But, in the case of self-paced learning, each student takes time and chooses the most appropriate approach from the available learning methods. Not only can the student change the pace of learning according to his ability to comprehend, but he/she can also choose the appropriate one from the various learning resources and interact more meaningfully with the subject.

For example, the introduction to a new topic could be a music video, a pdf of a research paper, an experiment, or a group activity. In the traditional learning method, all learners are compelled to do one or two of these within a specified time. But in the self-paced learning method, the student can choose and take advantage of all the possibilities available to him. Teachers can be multi-directional in many ways, incorporating a wide variety of learning materials and related activities into each learning environment. The general nature of self-paced learning is to open up all avenues for accessing and behaving in the text accordingly, based on the basic premise that each learner is of a different type. The pace of learning is determined by the learner, which also means that the study separates itself from its traditional order and narrow environment. The learner can choose another time to concentrate instead of a noisy time and use a more comfortable open space instead of a closed classroom. One can watch the rest of the lesson on laptop or TV at home, then watch it on mobile phone while traveling by bus and repeat the required modules in between other activities. Here, the learning process is freed from the limitations of physical conditions.
Reformulating the Examinations
The possibility of rethinking the examination procedures will also become evident in this case. The present method of examination, which is generally a memory test of past lessons to be completed in each time, will become irrelevant in e-learning. It is because, in the self-paced learning, the student is asked to self-evaluate after he/she has spent the required amount of time in each lesson. Instead of taking a quiz on that subject, one needs to use more scenario-based modelling assessment tools to find out if the knowledge has been acquired and how the student will apply it in a particular situation. This will make the study and the exam more complementary and the learning process more productive.

Key Challenges
- Given the potential for self-paced learning, it cannot be considered an effective, innovative model for all learning needs. Self-paced learning methods have many limitations in primary education. In the self-paced environment mentioned earlier, the additional responsibility that the learner must assume cannot be handled by young children. This means that different self-paced learning models will be required at various levels, ranging from primary to higher education.
- Another limitation of the self-paced learning approach has been the difficulty of having multiple learners in the same class (cohort) at different stages of learning at the same time. This can make the learner anxious to spend more time on one module and those who complete the same module faster can become lazy. Unbalanced learning levels can also confuse the facilitator.
However, with imaginative intervention, the situation can be put to good use. Those who want to complete the module can activate their learning through peer learning from those who have already completed it. The effectiveness of ‘peer learning’ has already been proven one and widely accepted. In addition to making a positive difference in learning, it can also lead to improved mutual understanding and teamwork. Those who have completed the module can perform other related activities besides peer teaching. Thus, if the framework of the old classroom is changed, the learning environment will be enhanced, and different possibilities will be opened for each.
- Also, we know that the e-learning cannot be used for all subjects. Many subjects can be studied effectively only through fieldwork, public interface, and experiments. Moreover, learning in a completely virtual environment is not a complete model, even for subjects that do not seem to require such offline lessons. Some subjects must be studied in their natural living environment. There are no alternatives to direct interaction between individuals.
So, what are the vast possibilities of self-paced learning as a pedagogy?
The hybrid model that we are now adopting mostly works by running one part of the curriculum through the traditional classroom method and the other part through e-learning / online classes. As indicated earlier, learning models that adopt a completely virtual approach do not have a universal character. So, the hybrid model can be continued with appropriate amendments in it.
Reason being that the current hybrid models are (almost always) shaped by the principles of classroom learning. For instance, take attendance before an online class, even set a timetable to watch a previously recorded classroom video, and send a photo of homework via WhatsApp etc).
Many of the possibilities mentioned earlier that open-up the pedagogy of self-paced learning can be effectively incorporated into the hybrid model.
Additionally, we should explore the possibility of innovative pedagogy by giving learners the right to self-determination at different time points in a course, applying new assessment models, providing a variety of learning resources, and promoting peer learning. Else, as long as the pedagogy of classroom learning remains at the centre of the hybrid model, the potential for e-learning will greatly be limited and we would miss the opportunity to address the inadequacies of the old learning methods.
The first step in taking advantage of this opportunity is for teachers to abandon the mace of power.
The academic world must then take on the responsibility and move into the broader role of facilitator without any sense of insecurity and to explore the possibilities of transforming the structure of learning in an atmosphere of collective responsibility and mutual trust. Yes, another teaching is possible!
]]>A world where the patterns of consumption, production and employment are going to be markedly different. Most jobs are experiencing a fundamental transformation. While some jobs are at the cusp of redundancy and others are growing rapidly, existing jobs are also going through a change which will require different skills sets to continue in them. In most of mundane and repetitive areas, a new generation of automated systems will replace humans. The smart machines will also become our collaborators in more complex areas, thereby augmenting our own skills and abilities. Smart machines will also establish new expectations and standards of performance.
Over the next decade, as it is predicted, new smart machines will permeate into offices, factories, and homes and become ubiquitous the same way electricity has become in our lives today. As these machines replace humans in some tasks, and augment them in others, their long term impact may be less obvious. The question remains is what would human ingenuity now bring about?
Framework for Understanding the Future of Work
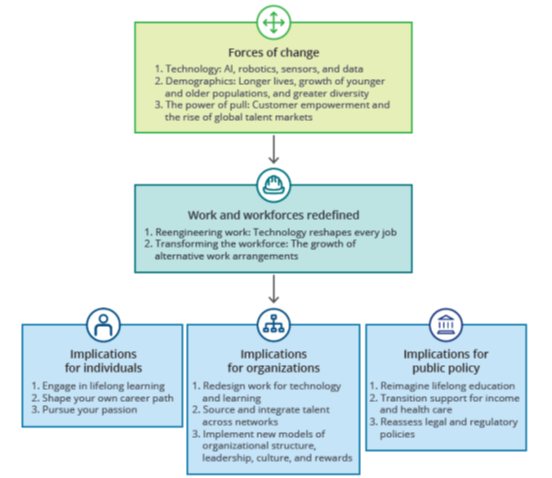
The Forces of Change impacting the Future of Jobs
As described earlier, the set of forces that are majorly impacting the future of jobs can be classified in three groups:
Forces of Changes in Technological Spectrum
Advances in computing power and Big Data: The power of crunching huge amounts of data using immense computing power which is available today develops ability to discern patterns that can both supplement and supplant human beings.
Internet of Things: The use of remote sensors, communications, and processing power in industrial equipment and everyday objects will give rise to what is being called ‘cyber physical systems’ where powers of machine and human beings intertwine to create force multiplier.
Advances in Robotics: One of the manifestations is that robots with enhanced senses, dexterity, and intelligence can be more useful than human workers in manufacturing, as well as in a growing number of service jobs, such as cleaning and maintenance. Further, with development of autonomous vehicles, whole set of jobs related to motor industry will get transformed.
Advances in Artificial Intelligence: The developments in AI, including machine learning, and natural user interfaces are making it possible to develop ‘chatbots’ that can potentially replace knowledge workers.
Advances in 3D Printing: A range of technological advances in additive manufacturing technology is transforming the whole manufacturing industry. This leads to rapid prototyping and on-demand customized manufacturing in low volumes.
Forces of Change in Demographics
Longevity and ageing societies: The composition of the global workforce is changed by shifts in demographics. Largely, in developed countries, people are living longer than ever. As a result, the population is becoming both older and younger, with individual nations becoming more diverse. This implies that jobs of the future would have to cater to both ends of the population spectrum.
Young demographics in emerging markets: The younger generations are largely concentrated in developing economies. As, many parts of the developing world are experiencing rapid population growth and face a very different demographic challenge than advanced economies. Many emerging countries continue to scale up the skills sets and provide high-quality education. This creates a tectonic shift in the global distribution of talent.
Forces of Change in Work environments and Flexible Working arrangements
Due to global shift in talent pool, both institutions and prospective workers now have access to global markets. Remote working, co-working spaces and web-conferencing are a few innovative value additions enabled by networks and platforms opening up new possibilities for the way each interacts with the other. This opens up opportunities for creative work done by smaller organizations with linkages to external consultants and freelance workers spread across geographies.
Skills Needed for Future Jobs

Sense Making: With the advances in technology, a lot of routine and mundane manufacturing and service job could be taken over by smart machines. However, there would be higher order jobs which require thinking skills, which could not be translated to a machine code. Such skills are generally called as ‘sense-making skills’. These are the abilities that human develop to create unique insights, that are critical to decision making tasks.

Social Intelligence: The social intelligence is the ability that humans have which enable them to quickly understand the emotions of people around them and based on that moderate the tonality of speech and the body language. This is important for humans to create relationships of trusts which are important for collaborative working. The skill that is difficult to build in robots and other smart machines is the intuitive ability to feel the emotions of others around. This will continue to give human workers an advantage over machines. Therefore, social intelligence is something that should be assiduously cultivated.

Novel and Adaptive Thinking: Jobs of the future would require the ability of being able to adapt as per the situation demands. This ability means, say in context of discovering a new drug, creation of a new synthesis route from the existing bio-chemical reagents. This is what is termed as novel and adaptive thinking. This ability again creates employability of humans in the higher order jobs.

Cross-Cultural Competency: Tomorrows’ organizations would not only operate in a globally connected fashion, but also have diversity as their core competency. This implies that people must have skills to not only be able to operate in different geographies, but also with people of diverse backgrounds — age, skills, disciplines, and working styles. This is what it means to have cross-cultural competencies.

Computational Thinking: With the advent of Big Data and Analytics, the next generation of human workers must develop computational thinking ability. This ability implies how to make sense of the huge amount of data and its analysis to bring out models that guide the decision making process.

New-Media Literacy: Our social life is dominated by user generated content which is visually rich. Therefore, the ability to fluently understand the rich media content such as videos, animations would be a key skill per se. The ability to use and understand immersive and visually stimulating presentation of information would be a key aspect.




Virtual Collaboration: In the future, the work environment would largely become virtual and the connective technologies make them so much easier. This will require developing new set of competencies, whereby members of virtual teams should become adept at improving productivity and well being of the group.
Prescriptions for Academic Institutions
With the changing times, the educational institutions at all levels – primary, secondary, and tertiary should also undergo a transformation and give up the hang-ups of the past. Since the landscape in which the future graduates of these institutions will find themselves, they will have to make a directional change. Some of these areas could be:
- The curricula must embed in the learning outcomes the abilities such as, critical thinking, design mind set, and analytics capabilities. The curriculum should also integrate use of new media so as to ingrain this skill among the learners.
- The experiential learning component must give importance to soft skills such as the ability to collaborate, work in teams, comprehension of social cues and adaptive responsiveness.
- Life-long learning should be the new credo and institutions must reach out to working adults to re-skill them for emerging job requirements.
- Integration of the multidisciplinary training that enables learners to develop skills and knowledge in a wide range of subjects by embedding liberal studies in technical and business education.
]]>